Chain abstraction and the future of Web3 UX: Insights from Decentralized Mic
Discover how chain abstraction can remove complexity from Web3, improving user experience and enabling multichain applications. Featuring insights from Agoric, Polytope Labs, Sommelier, and Polkadot.
 By Joey Prebys•May 14, 2025
By Joey Prebys•May 14, 2025
What you can expect
- A clear explanation of what chain abstraction means in Web3
- Why user experience (UX) is the biggest challenge and opportunity for blockchain
- Insights from Agoric, Polytope Labs, and Sommelier Protocol leaders
- How Polkadot’s XCM and shared security enable chain abstraction
- Why chain abstraction is essential for scaling Web3 to mainstream users
Despite years of technical progress, Web3’s biggest barrier remains simple: it’s too complicated to use.
For blockchain to go mainstream, the underlying complexity must disappear so users can focus on outcomes, not infrastructure. That’s the promise of chain abstraction.
A recent episode of The Decentralized Mic, moderated by Braille CEO Benoit Campagnaud, brought together leaders from Agoric, Polytope Labs, and Sommelier Protocol to explore how chain abstraction can finally deliver the UX breakthrough Web3 needs—and why now is the right time.
What is chain abstraction in Web3?
Chain abstraction allows users and developers to interact with applications and assets across multiple blockchains without needing to understand or manage the underlying infrastructure.
As Dean Tribble, CEO of Agoric, explained:
“When I buy a hamburger on DoorDash, I don’t care if the restaurant runs on Google Cloud or Amazon. I just want a hamburger.” — Dean Tribble
That’s the goal for Web3. Users should be able to swap, stake, borrow, or buy NFTs without thinking about which chain they’re using or how the transaction works under the hood.
Crypto-native users already know the power and potential of blockchain. But if it stays time-consuming or overly complex, adoption will never scale. Chain abstraction could change that.
How does chain abstraction improve user experience in Web3?
Today, users often have to navigate multiple wallets, bridges, and complex signing processes just to move assets between chains or use different dapps. Chain abstraction simplifies that by creating unified interfaces and processes that handle cross-chain complexity behind the scenes.
Seun Lanlege, Co-founder of Polytope Labs and lead developer of Hyperbridge, pointed to stablecoin bridging as a real-world example where chain abstraction is already benefiting users.
“Stablecoins act like reserve assets. Bridges and stablecoins are a perfect match because people expect to use them everywhere easily.” — Seun Lanlege
Zaki Manian,Co-founder, Sommelier Protocol, echoed this, adding that Circle’s Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP) has done more to improve cross-chain UX than almost any other effort so far.
How does chain abstraction address blockchain fragmentation and interoperability?
The explosion of blockchains, rollups, and appchains has led to liquidity fragmentation and user friction. Without chain abstraction, users have to manually bridge assets, manage multiple wallets, and navigate inconsistent interfaces.
Chain abstraction connects these fragmented ecosystems, enabling assets and transactions to flow smoothly between them.
Zaki noted that while stablecoins and perpetual markets are becoming more chain-abstracted, some areas like memecoin casinos have resisted this trend, highlighting both the progress and remaining challenges.
What technologies and protocols enable chain abstraction?
Several technologies support chain abstraction today:
- Cross-chain messaging protocols like Polkadot’s XCM and Cosmos’s IBC
- Bridges such as Hyperbridge, IBC Eureka, and Circle’s CCTP
- Orchestration tools that coordinate actions across chains
- Account abstraction proposals (e.g., Ethereum’s EIP-7702) that allow flexible authorization models
Polkadot’s approach of aggregating security and messaging through the Polkadot Chain is specifically designed to support chain abstraction at the protocol level. This contrasts with Cosmos’s peer-to-peer model, where chains negotiate connections individually.
“With Polkadot, you connect to the hub and immediately become interoperable with all these chains—and you get security as a byproduct.” – Seun Lanlege
How is chain abstraction different from account abstraction?
Chain abstraction focuses on hiding the complexity of cross-chain interactions, allowing users to engage with multiple blockchains through a single, simple interface.
Account abstraction, by contrast, lets users customize how transactions are authorized. For example, enabling smart contracts or authorized agents to execute transactions on the user’s behalf.
The two are complementary. As Zaki and Dean discussed, Ethereum’s upcoming EIP-7702 will enable account abstraction use cases that support chain abstraction, such as intents that let users request actions without manually executing every step.
What are the security implications of chain abstraction?
Security is a key concern. As Dean noted, using smart contracts with high integrity is critical. Users should avoid relying on opaque, off-chain agents to execute actions on their behalf.
Instead, well-designed smart contracts and trusted orchestration layers (like those being built on Agoric, Hyperbridge, and through Polkadot’s shared security model) will enable safer cross-chain operations.
Which projects or protocols are leading the development of chain abstraction?

According to the panelists, leaders in this space include:
- Polkadot, with XCM and rollup interoperability
- Cosmos, with IBC and related tooling
- Agoric, focusing on smart contract orchestration
- Polytope Labs / Hyperbridge, enabling authenticated cross-chain messaging
- Sommelier Protocol, working on cross-chain vaults and liquidity solutions
Both Polkadot and Cosmos were cited as ecosystems offering pragmatic, user-centric approaches to chain abstraction, though their philosophies differ.
“The explosion of appchains has driven people to realize that abstraction across chains is important, because there are now hundreds of them.” – Dean Tribble
How does chain abstraction impact liquidity and resource management?
Chain abstraction reduces liquidity fragmentation by allowing assets to move freely across ecosystems.
Zaki explained that liquidity abstraction has improved dramatically in recent years. This allows users to interact with their balances and deploy capital without worrying about which chain it’s on.
It also helps developers avoid splitting user bases and liquidity pools across multiple deployments.
What challenges remain for achieving full chain abstraction?
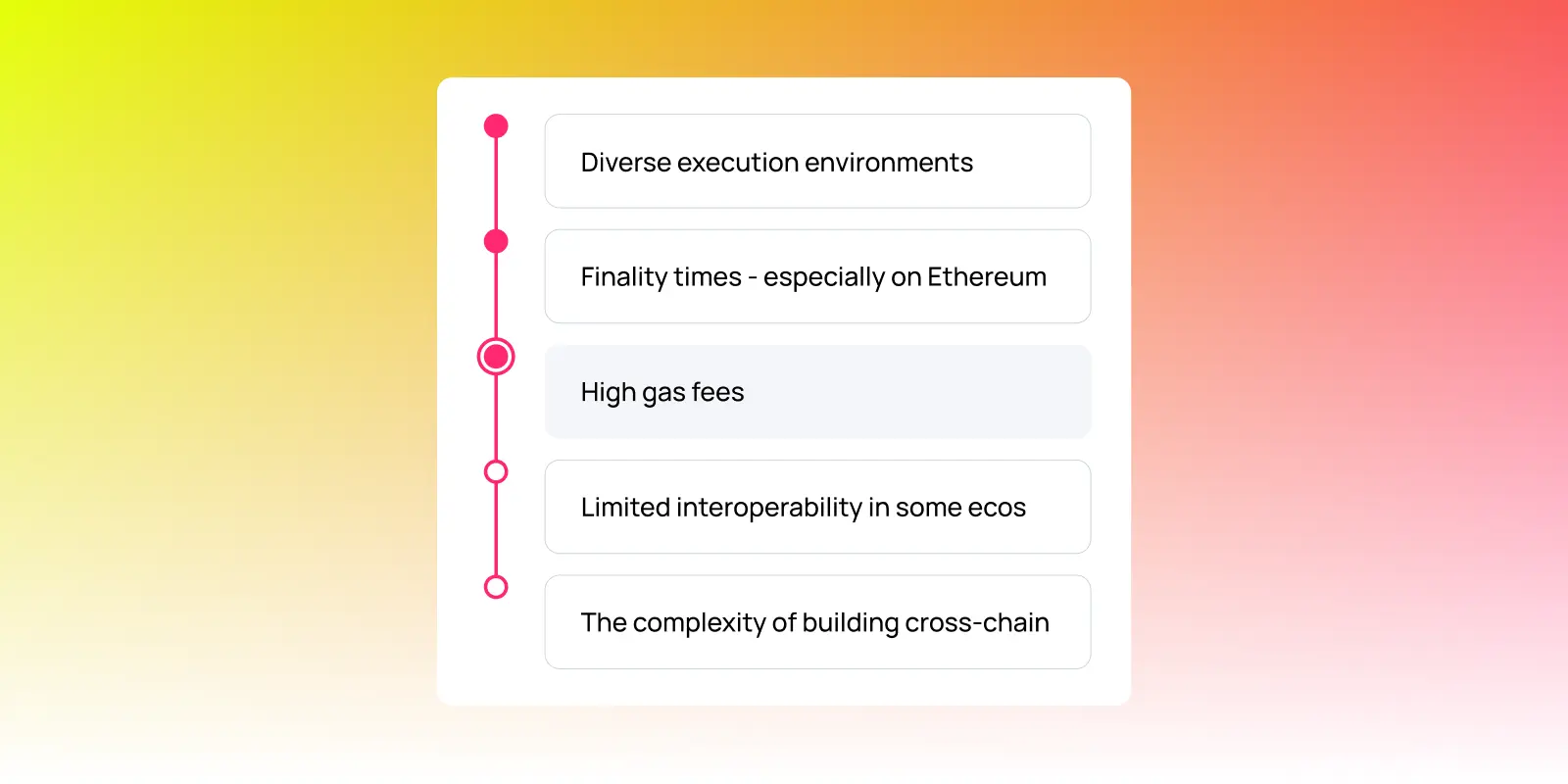
Several challenges were identified:
- Diverse execution environments
- Finality times—especially on Ethereum
- High gas fees
- Limited interoperability in some ecosystems
- Complexity of building cross-chain intents and orchestration layers
While some areas are progressing well, cross-chain orchestration remains challenging for more specialized use cases.
Key takeaway: chain abstraction is UX
The core message from The Decentralized Mic was clear: chain abstraction is ultimately about creating the kind of UX users expect from Web2.
No one wants to think about chains, bridges, or wallets. They want to stake, swap, borrow, buy NFTs, or dollar-cost average into positions—simply and safely.
As the panelists made clear, Polkadot’s approach—shared security, hub-based messaging, and pragmatic solutions—is well-aligned with this vision. While challenges remain, the multichain future is moving rapidly from concept to reality.