What is decentralized AI? A beginner’s guide to blockchain-powered intelligence
Decentralized AI distributes data, compute, and control. It makes AI more open, private, and community-driven. Learn how Polkadot supports this shift.
 By Joey Prebys•June 20, 2025
By Joey Prebys•June 20, 2025
What you can expect
- What decentralized AI is and how it differs from centralized systems
- Why decentralized AI matters in today’s digital landscape
- How decentralized AI systems work in practice
- The benefits and challenges of decentralized AI
- Where decentralized AI is being used today
- How Polkadot supports a decentralized AI future
AI is everywhere. It helps us analyze dense documents in seconds, brainstorm business ideas on the fly, transform ourselves into characters from our favorite movies, and it even answers the questions we’re too embarrassed to ask out loud.
But for all its usefulness, AI also raises serious concerns.
Today’s most popular and powerful models are controlled by a handful of tech firms. Their inner workings are opaque. We don’t know where the training data comes from, how decisions are made, or who benefits when the models improve. Creators often go uncredited and uncompensated. Biases creep in unnoticed. And the tools shaping our future are being built behind closed doors.
That’s why people are starting to push back. There’s growing concern about surveillance, misinformation, lack of transparency, and the fact that a few companies control how AI is trained and who reaps the rewards. These fears are fueling demand for systems that are more transparent, privacy-preserving, and open to broader participation.
Decentralized AI (DeAI) offers a solution. These systems distribute data, computation, and governance, making AI models more accountable, transparent, and inclusive. Contributors can be fairly rewarded for their input. Communities can help shape how these powerful tools work.
And Polkadot is already supporting this future, offering the infrastructure for ethical, decentralized AI systems that work for everyone, not just a few gatekeepers.
What is decentralized AI and how is it different from centralized AI?

Most of today’s AI runs on centralized systems. A single company collects the data, trains the model, and controls the output. These systems are typically closed off to public input or oversight, and users have no way to know how the model was built or what biases it might harbor.
Decentralized AI works fundamentally differently. Data is shared across nodes, models are governed by communities or protocols, and updates happen through transparent processes. Instead of a black box controlled, you get a system built collaboratively in the open, with clear rules and incentives for participation.
Think of it like this: centralized AI is like a museum run by a private foundation. You can walk through the curated exhibits and even see your own data reflected in some of the art, but you have no say in how the collection is built. You are not credited or compensated for what you contribute. The decision-making is opaque, and most of what happens behind the scenes stays hidden.
Decentralized AI, on the other hand, is like an open-air art exhibition built by a global community. Artists, historians, and citizens all contribute ideas, share data, and help curate the collection. Every contribution is traceable and transparent, and contributors are rewarded for their input. If your work improves the exhibit, you get something back.
This kind of architecture supports stronger user protections and fosters greater accountability—two of the most pressing needs in today’s AI landscape.
Why is decentralized AI important?
Centralized control over AI raises serious concerns. When a handful of companies own the models, they also control what those models learn, how they behave, and who gets access. This creates several problems:
- Power concentration: A few companies control AI development with little public oversight.
- Algorithmic bias: Limited data and perspectives lead to unfair, exclusionary systems.
- No user control: People contribute data but get no credit, compensation, or say in how it’s used.
- Slower innovation: Centralized control limits experimentation and diversity in AI models.
Decentralized AI shifts the balance. By distributing ownership and control, it opens the door to more transparent, equitable, and innovative AI systems. Contributors from around the world can help shape the models and ensure they reflect a wider range of perspectives.
Transparency also plays a key role. Many decentralized AI systems adopt the principles of open-source AI, where the code and training methods are publicly accessible. This makes it easier to audit models, identify problems, and build trust.
However, open-source AI is not always decentralized. A model can be open-source while still relying on centralized infrastructure or lacking privacy-preserving mechanisms. Still, both approaches share important traits like transparency, accessibility, and community input.
When users don’t have to give up control of their data to participate, they’re more likely to get involved and benefit from the results.
Decentralization is not a silver bullet, but it does open the door to building AI systems that are more aligned with public interests and less controlled by private agendas.
How does decentralized AI work?
Decentralized AI replaces centralized control with distributed systems. Rather than relying on a single company’s servers, these models are trained, refined, and deployed across a network of independent nodes. This helps prevent single points of failure, makes systems more transparent, and invites broader participation.
What technologies power decentralized AI?
Federated learning lets AI models learn from data without collecting it in one place. Instead of sending sensitive information to a central server, the model is trained locally—on your phone, laptop, or another device—and only the learnings (not the raw data) are shared. These small updates are then combined to improve the overall model. For example, your phone’s keyboard might learn how you type and suggest better autocorrections without ever uploading your messages. This means the system can keep getting smarter while your private data stays on your device. This technique isn’t unique to decentralized AI, but it aligns well with its goals: keeping data private and distributed.
Distributed compute builds on this idea by spreading the heavy lifting of training and running AI models across many different machines in the network. It’s like having thousands of smaller computers, each taking on a piece of the work, rather than relying on one giant server. This makes the system faster, more efficient, scalable, and resilient.
Cryptographic tools like zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) can also help protect privacy by verifying data or actions without revealing the underlying information, ensuring systems remain trustworthy and secure even when distributed.
How blockchain supports decentralized AI
To make this all work, decentralized AI systems need a way to coordinate tasks, secure data, and reward contributors. Blockchain provides this critical foundation.
Smart contracts automate processes—like paying contributors or updating models—based on transparent, predefined rules that execute without human intervention.
Oracles serve as bridges between blockchain networks and the outside world, feeding in real-world data that AI models might need (such as weather, prices, or sensor readings).
Decentralized storage solutions keep training data and model files accessible across the network. Unlike traditional servers, these systems store data across many nodes, making them significantly more resistant to tampering, censorship, or single points of failure.
Polkadot: built for modular artificial intelligence
Polkadot’s unique architecture supports these kinds of systems by design. It allows different networks to specialize in different tasks—such as privacy, compute, or governance—while remaining interoperable. This modular approach makes it possible to scale decentralized AI systems without sacrificing flexibility, security, or performance. Different components can be optimized for their specific functions while working together as a cohesive whole.
What about decentralized AI agents?
One emerging concept is the decentralized AI agent: a small, autonomous program that helps coordinate tasks within the network. These intelligent agents can handle things like matching computational jobs to available resources or routing data between trusted sources. We'll explore this concept more in a future post.
What are the benefits of decentralized AI?
Decentralized AI isn’t just a technical shift. It’s a new way of building systems that reflect shared human values: privacy, transparency, fairness, and participation. By distributing control, it unlocks benefits that closed models struggle to offer.
- Better privacy: Keeps sensitive data local through techniques like federated learning, on-device training, and cryptographic methods such as zero-knowledge proofs.
- Built-in transparency: Open systems make it easier to audit models, track decisions, and identify bias.
- Shared governance: Communities help shape the rules, incentives, and evolution of the models.
- Fair economic incentives: Contributors are rewarded for their data, compute, or model improvements.
- Reduced bias: A broader set of contributors means more inclusive perspectives and fewer blind spots.
- More resilience: Without a single point of failure, decentralized systems are harder to compromise or shut down.
Polkadot supports these benefits through its modular architecture. Different networks can specialize in specific aspects like privacy, compute, or governance, then work together seamlessly. This flexibility makes it possible to scale decentralized AI without compromising security, user agency, or system performance.
What are the challenges and limitations?
Decentralized AI holds promise, but it’s not without challenges.
- Scalability: Training large AI models requires substantial compute power. Distributing that work across many nodes can slow things down or create coordination hurdles.
- Compute intensity: Even with distributed systems, AI models are resource-heavy. Running them across devices or nodes can strain bandwidth and energy use.
- Regulatory uncertainty: As governments debate how to regulate AI, decentralized systems add complexity. Who is accountable when a model goes wrong? What happens when nodes operate in different jurisdictions?
- Fragmentation: Without centralized oversight, decentralized systems can splinter. Competing standards or uneven participation may make it harder to build cohesive tools.
- Security and reliability: Trustless systems can still be vulnerable. Bad actors might try to manipulate data, poison models, or exploit weak points in the network.
- User experience complexity: Decentralized systems often require users to manage private keys or navigate multiple interfaces, creating barriers to mainstream adoption.
These are real concerns, but they’re not insurmountable. Polkadot’s modular architecture helps address many of them by offering robust shared security to eliminate weak points and native interoperability for seamless coordination across networks. Individual networks can focus on specific challenges while still collaborating across the ecosystem. This flexibility supports responsible growth, with built-in safeguards and shared accountability.
Where is decentralized AI used today?
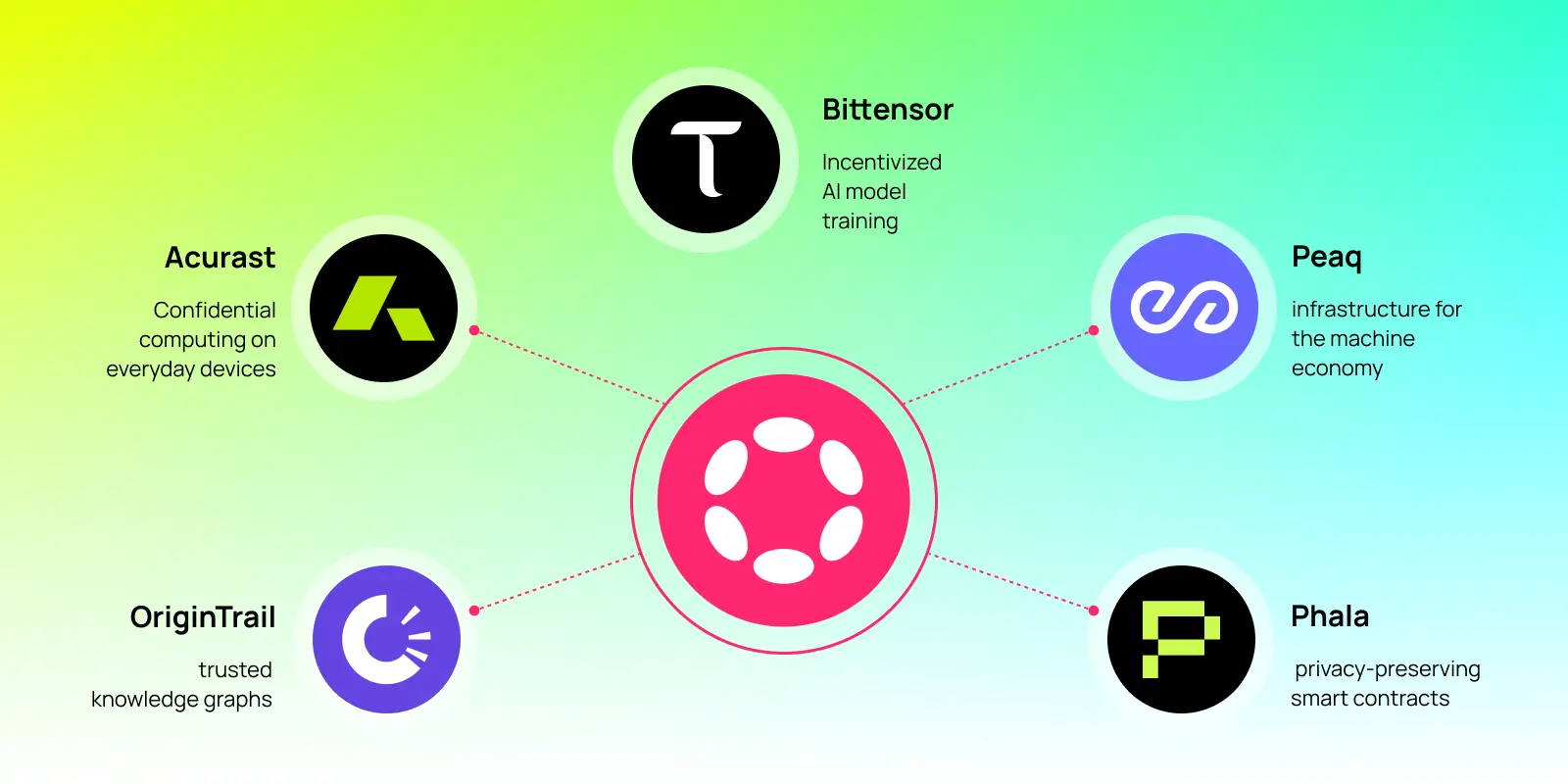
Decentralized AI is not just theoretical. Projects across Web3 are already demonstrating how distributed intelligence can power real-world applications, with Polkadot playing a key role in enabling this future. Here are five projects building decentralized AI on Polkadot.
Acurast: confidential computing on everyday devices
Acurast lets anyone turn old phones and other devices into part of a secure, decentralized cloud. You can get rewarded for offering your unused compute power. Developers use that power to run privacy-sensitive tasks without relying on Big Tech servers, creating a more private, people-powered internet.
OriginTrail: decentralized knowledge graphs
OriginTrail runs on a decentralized knowledge graph, which connects and organizes trusted data across supply chains, education, and beyond. It’s like a public library of facts that anyone can contribute to or check, but no single company controls. This helps verify things like where a product came from or whether a certificate is authentic, without relying on a central authority.
Phala: privacy-preserving smart contracts
Phala Network is building the privacy layer for Web3. It lets developers run smart contracts in a confidential computing environment, so sensitive data like identity or health information stays private even while apps use it. Think of it as a secure workspace for your data that the app creator cannot see.
peaq: infrastructure for the machine economy
peaq helps power decentralized physical infrastructure by letting people and devices earn rewards for completing real-world tasks. Think of it like a gig economy for machines. A robot might charge an electric vehicle, or a sensor might report air quality, and both can get paid through the network. Peaq makes it easy to coordinate and reward this kind of machine-driven work.
Bittensor: incentivized AI model training
Bittensor creates an open marketplace where AI models compete and collaborate to provide the best outputs. Anyone can join the network to contribute computing power, train models, or evaluate performance. The system uses token incentives to reward useful contributions, creating a self-improving, censorship-resistant AI economy that doesn’t rely on centralized control.
Beyond Polkadot
Other notable projects include Ocean Protocol, which enables secure data sharing for AI training, and Fetch.ai, which focuses on autonomous economic agents. Together, these examples show the wide and rapidly growing ecosystem of decentralized AI across blockchains.
Polkadot is building the future of decentralized AI
Decentralized AI isn’t just a technical shift. It’s a values shift. It challenges the idea that intelligence should be controlled by a handful of companies, offering a more open, accountable alternative. These systems distribute power, protect privacy, and invite global participation in shaping the tools that shape our world.
Blockchain makes this possible. By coordinating updates, securing data, and rewarding contributors, it provides the foundation for AI systems that are transparent by design. And Polkadot adds another layer: modular infrastructure that enables specialized networks to excel at specific functions while benefiting from Polkadot’s native features and maintaining seamless interoperability across the broader ecosystem. This flexibility allows decentralized AI systems to evolve and scale without sacrificing security, performance, or user agency.
From confidential computing to decentralized data curation, the Polkadot ecosystem is already home to projects that put these principles into practice. And we’re just getting started.
Ready to explore decentralized AI in action? Learn more about how Acurast, Phala, OriginTrail, and others are building the future on Polkadot.